Section 8. Debut of the Toyopet Crown, a Full-Fledged Passenger Car
Item 3. Development of a Full-fledged Passenger Car, the Toyopet Crown
Development of the R engine
From the outset, there were comments to the effect that the S engine (fitted in the Model SB compact truck launched in April 1947) delivered insufficient engine power for the size of the vehicle body. In response, Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. decided at the beginning of 1948 to develop a prototype 1,500cc Model P engine (Table 1-39) with the same side valve (SV) format as the S.
Table 1-39. Comparison of Main Characteristics of the S, P, and R First Prototype Engines
|
|
S Engine (1947)
|
P Engine (1948)
|
R Engine First Prototype (1951)
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Model
|
Water-cooled, inline 4-cylinder, single valve
|
Water-cooled, inline 4-cylinder, single valve
|
Water-cooled, inline 4-cylinder, overhead valves
|
|
Bore×Stroke
|
65×75 mm
|
Unconfirmed
|
75×82 mm
|
|
Total engine displacement volume
|
995 cc
|
Approx. 1,500 cc (details are unknown)
|
1,449 cc
|
|
Maximum output
|
27 hp/4,000 rpm
|
40.5 hp/3,800 rpm
|
44.6 hp/4,000 rpm
|
- Source:
- S Engine: 'Toyopet (Small Truck) Specification Sheet', Toyota Technology, June 1, 1948
P Engine and R Engine First Prototype: 'Creation of the R Engine', Toyota Technology, January 1, 1954
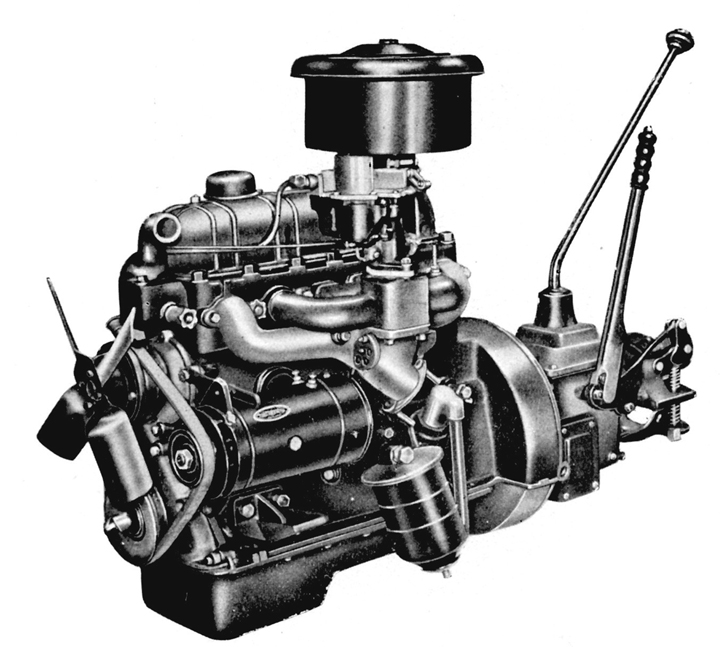
Later, analysis of data from operating tests and other factors led to a switch to the overhead valve (OHV)-type with its superior performance, and in January 1951, the first prototype of the R engine was completed. After refitting the Model SB truck with the new R engine and checking its performance, plans for mass production of the engine were settled and the design was completed in March 1952.
However, in May of the same year, Senior Managing Officer Eiji Toyoda proposed a change to the bore and stroke dimensions and it was decided to alter the design to bring it as close as possible to the square format (in which both the bore and stroke dimensions are equal). The reasons for this included the wish to avoid as far as possible an increase in the height and the center of gravity of the OHV engine, the ability to increase the engine speed, and the fact that the engines fitted in newly designed non-Japanese vehicles were almost all of the square format. The specifications of the final R engine, the design of which was completed in August 1952, are presented in Table 1-40.
Table 1-40. Specifications of the R Engine (1952)
|
Item
|
Description
|
|---|---|
|
Model
|
Water-cooled, inline 4-cylinder, overhead valves
|
|
Bore×Stroke
|
77×78 mm
|
|
Total engine displacement volume
|
1,453 cc
|
|
Compression ratio
|
6.8:1
|
|
Maximum output
|
48 hp/4,000 rpm
|
|
Maximum torque
|
10 kg-m/2,400 rpm
|
- Source:
- R Engine: Toyota Technology, January 1, 1954
The R engine adopted the OHV format which had been a Toyota tradition since the A engine. The parts and design had a wide range of points in common with the B engine in terms of mechanisms and devices, including the Carter downdraft carburetor and the paper filter air cleaner.1 Resembling in external appearance the B engine, it was recognizable at a glance as a Toyota-developed engine.
The vehicle models launched with the R engine were the RH Toyopet Super passenger car (released in September 1943 as a modified version of the Model SF passenger car) and the RK Toyopet truck with 1.25-ton load capacity (a modified version of the SG truck). Model RH passenger cars were of two types: one type manufactured by Kanto Auto Works, Ltd. (RHK) and the other by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (RHN). As previously, the design and production of the vehicle body were handled by the respective company, which made it difficult for Toyota Motor Co., Ltd. to undertake fixed pricing and quality assurance for these passenger cars.
Although the R engine had a 48hp output-a great increase on the S engine's 28hp-there was no major difference in fuel efficiency, making it a very economical vehicle. This output helped boost cruising performance drastically, so that representatives of the taxi industry who test-rode RH passenger cars judged it highly satisfactory in terms of riding comfort, power, and maneuverability.
For production, cutting-edge facilities had been put in place in the second half of the 5-Year Facility Modernization Plan, centering on the specialist machine tools of the Koromo Plant machining plant. In July 1953, immediately before the sales launch, a R engine line for monthly production of 500 units was completed. Development of another passenger car model to be fitted with the R engine began in January 1952.